Whether you consider carrots a fruit or a vegetable will depend on how you look at it. Generally, a fruit is a food that contains seeds, while a vegetable is one that contains stems, leaves, flowers, or roots.
Whether you eat them as a vegetable or as a fruit, carrots are a healthy addition to your diet. They are high in fiber and have a good amount of lutein and beta carotene. Also, they are a good source of sodium.
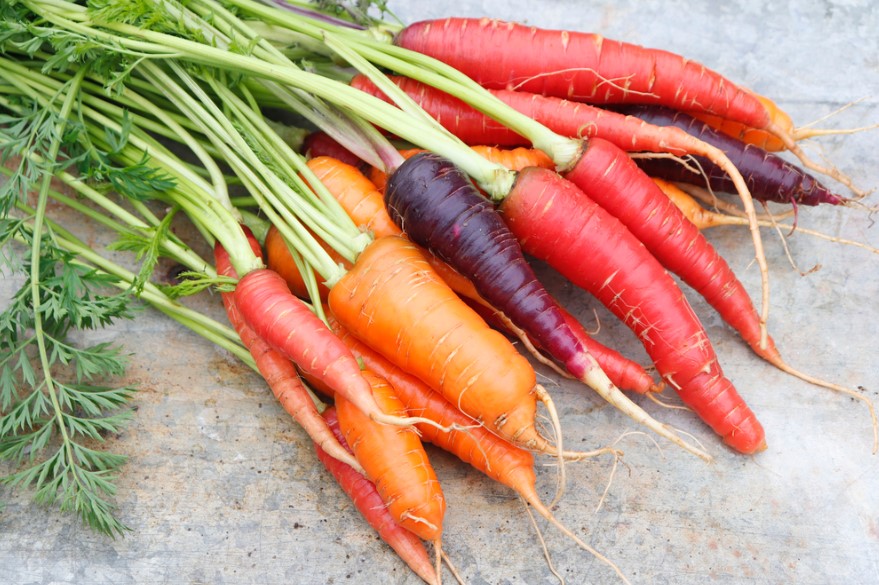

Are Carrots a Fruit or a Vegetable
Generally, the answer to the question is that carrots are a vegetable. However, it’s important to remember that carrots are not fruits. Biologically, a fruit is a seed-bearing structure, while a vegetable is a plant part eaten as food.
Carrots were originally cultivated for their medicinal properties. They were used to treat toothaches and skin disorders. They were regarded as a good source of Vitamin A, which is needed by the immune system to help fight off infections. Carrots also have a high level of beta carotene, a powerful antioxidant. In addition, carrots are rich in fiber, which helps to keep you full.
Carrots are popular for their orange color and sweet taste. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiled, steamed, roasted, or pureed. They are also delicious in dips and salads.
Carrots are a good source of fiber, potassium, and vitamin A. They are also a good source of beta carotene, an antioxidant that helps to prevent cancer. In addition, carrots contain lutein, which is important for eye health. This nutrient is also linked to reduced risk of age-related eye diseases.
Difference Between Fruits And Vegetables
Having a clear definition of the difference between fruits and vegetables can help you prepare a balanced diet that will support your health. Choosing the right food items can aid in proper digestion, as well as promote a strong immune system.
Both fruits and vegetables are essential parts of a healthy diet. They provide vitamins and minerals that are necessary for your body to function properly. In addition, they are good sources of fiber, which can help keep you feeling full and energized.
Vegetables are also a good source of Vitamin C, which helps with the repair and growth of your body tissues. Fruits are also rich in antioxidants, which can help fight disease.
Although there is no definitive answer to the question of the difference between fruits and vegetables, there are many foods that we often call vegetables that actually are fruits. In fact, you might not have noticed that they are actually fruits.
A fruit is a fleshy, seed-associated structure of a plant. Fruits are typically sweet, tart, or sour. They can also be bitter. Fruits are typically produced in springtime. Fruits can be eaten in their raw state, or they can be used as a dessert. Fruits are also used in juices and snacks.

Culinary Definition of Fruit and Vegetables
Whether it is in the grocery store or the kitchen, most people will be using the fruit and vegetable definition to describe what they are eating. Regardless of the actual definition, these foods are both high in vitamins, antioxidants and fiber. They are also low in calories and fat.
The culinary definition of fruit and vegetable is a bit ambiguous, relying on a variety of factors to differentiate between the two. One important factor is the flavor. Some vegetables have naturally sweeter tastes than others. Similarly, some fruits are more savory than others.
There is also a bit of debate about whether tomatoes are a fruit. Generally, tomatoes are classified as a vegetable. However, the plant products that make up a tomato aren’t actually part of the tomato plant. In fact, most people consider tomatoes a vegetable, while a few consider them a fruit.
Some fruits, like bananas, are actually vegetables, while others are botanically classified as fruits. Other fruits, like avocados, are considered botanical fruits.
The best way to determine whether a particular food is a fruit or vegetable is to ask the chef. This is a particularly important question for chefs because they are able to use the flavor profiles of a variety of different foods to determine whether or not they are a fruit or a vegetable.
Botanical Definition of Fruit and Vegetables
Defining what a vegetable and fruit are is a tricky proposition. Generally, a vegetable is defined as any part of a plant that is edible. Fruits are defined as any part of a plant that contains seeds.
The main difference between a fruit and vegetable is that a fruit is a seed-bearing structure of a plant, whereas a vegetable is any edible part of a plant. Fruits are often sweet and can be eaten raw or cooked. Vegetables, on the other hand, have a savory taste. Typically, vegetables are eaten as the main course, while fruits are served as a dessert.
Both fruits and vegetables are low in calories and are high in fiber. They are also an excellent source of vitamins. They are commonly used in desserts, snacks, and juices.
The botanical definition of fruit and vegetable is usually more precise than the culinary definition. Vegetables are defined as any part of a flowering plant that is eaten for nutrition. The botanical definition is based on scientific studies of plants. Fruits are classified by a number of characteristics, including taste, size, and sourness.
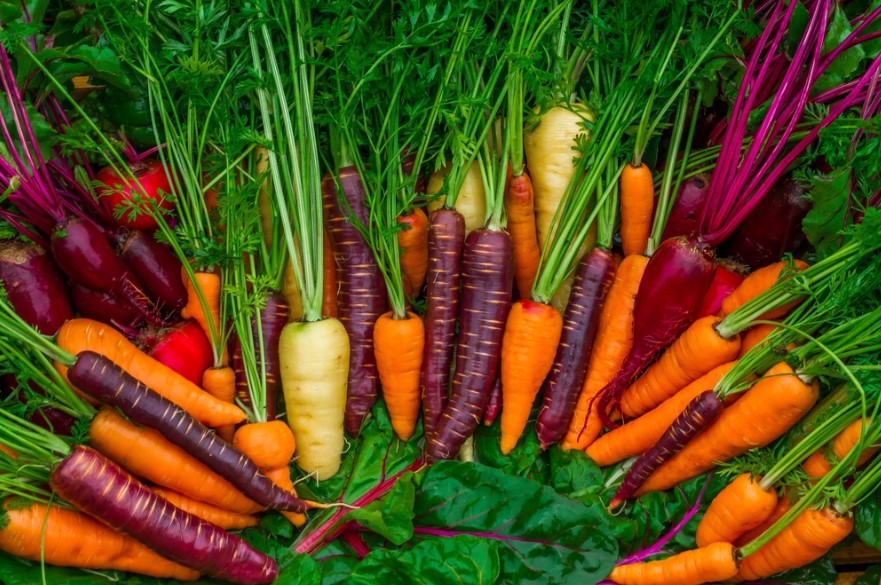

Could A Carrot Be Used As a Fruit?
Despite its name, carrots are a vegetable, not a fruit. Vegetables are any part of plants, from stems and leaves to roots and tubers, that are eaten as food. Fruits are plants that have seeds. Fruits include simple fruits such as apples and pears, and multiple fruits like pineapples, strawberries, and mulberries.
Carrots are a member of the family Apiaceae. They are a biennial plant that produces a taproot and a rosette of leaves. They grow quickly, and can be harvested within 90 days.
Carrots are high in fiber. This dietary fiber helps to lower blood sugar levels and promote healthy gut bacteria. Fiber also reduces the risk of constipation and promotes safe bowel movements.
Carrots are high in antioxidants, including phenolic compounds. These compounds are ubiquitous plant components, and may be important to human health because of their antioxidant potency. The main phenolic acid in carrots is succinic acid. However, hydroxycinnamic acids and chlorogenic acids are also present.
Carrots are a good source of Vitamin A and Vitamin C, which are important micronutrients for human health. Carrot roots contain 6,000 to 54,800 mg of carotenoids per 100 g.
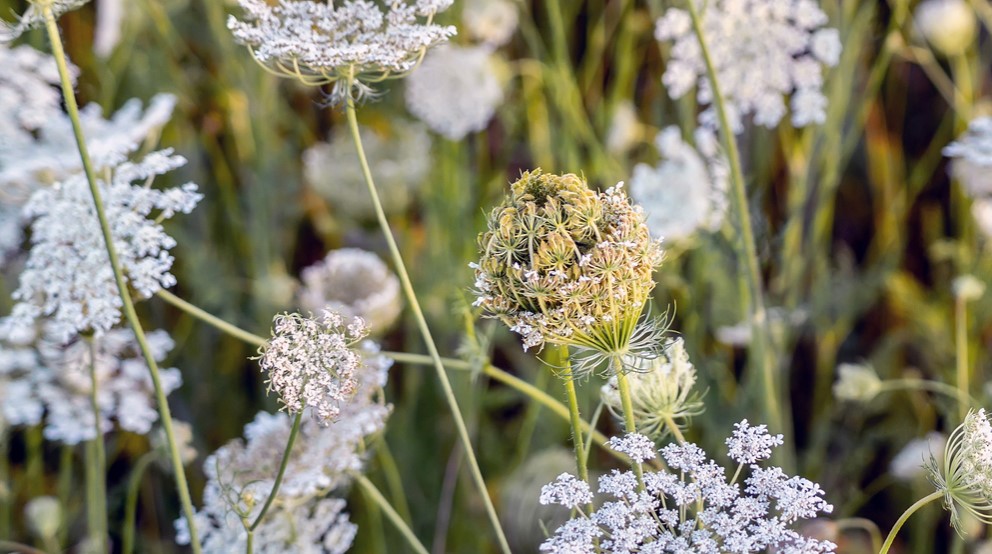

Where Do Carrot Seeds Come From?
Typically, carrot seeds are found in spent flower heads on the plant’s flower stalk. This is a very easy way to harvest them.
Carrots are in the Apiaceae family. They are considered biennial plants. They produce seeds during the second year of growth. The seeds can be stored for six years in ideal conditions.
Carrot seeds are stored in an airtight container in a cool and dark place. This helps protect them from sun and humidity. A cool storage location also increases their viability.
You can collect seeds by rubbing them between your hands. For a more thorough collection, you may want to use a fine mesh screen. You can then sieve the seeds to remove any chaff. Then you can place them in a glass jar.
Ideally, carrot seeds will last up to six years when stored properly. If you live in a dry climate, you may want to place the seeds in a silica gel pack or dry rice to reduce humidity.
In general, you want to start saving carrot seeds in the first year. That way, you’ll be able to enjoy their fruits for years to come.
Growth Cycle Of Carrot Plants
Unlike many other plants, carrots have a two-year growth cycle. The first part of this growth cycle is the seedling stage. During the seedling stage, the carrot plant relies on its internal food stores to power metabolic processes.
After the seedling stage, the plant continues to grow. It produces a central root, a taproot, and leafy green shoots. These shoots take up sunlight and reach toward the surface of the soil.
After the leafy green shoots are ready, the carrot plant produces flowering stems. The flowering stems are umbrella-shaped structures. The flowers are insect-pollinated. The pollen is transported from the flower to the stigma.
The umbels begin to flower, and each one will flower for seven to ten days. After the umbels complete flowering, the seeds will fall off the stem.
Carrot seeds are small. Each carrot plant will produce about 10,000 seeds. The carrot seeds take 10 to 12 days to germinate.
When the seedlings are ready, carrots should be pruned. The carrot plant should be pruned so that the weakest seedlings are removed. This will allow the carrot plant to concentrate its resources on setting seeds.

Can You Harvest Carrots After Flowering
Leaving carrots in the ground can be a viable option, but it requires proper care. Carrots are a biennial plant, meaning they go through two years of growth. The first year is vegetative, and the second year is when they flower. It takes about 50 to 75 days for carrots to mature.
When carrots flower, they produce a stalk that produces flat-topped clusters of tiny flowers. These flowers are similar to the ones found in umbellifer plants.
Carrots are also capable of producing seeds. The seed is produced on the tip of the flower stalk. They can be eaten or saved for future planting.
Carrots are also known for their long roots. They grow up to 12 inches in diameter. They have three to four true leaves.
Carrot seeds need light soil to sprout. They should be planted approximately 1/4 inch deep. Seeds should be spaced at least two to three inches apart in a row.
Carrots can overwinter in the ground if they are properly mulched. They require at least one inch of water per week. The best method for watering carrots is drip irrigation.

Uses For Carrots
Besides being a nutritious vegetable, carrots can be used in a variety of dishes. They are also easy to grow. They can be eaten raw or cooked. They are a good source of Beta-carotene, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Zinc, Iron, Potassium, Calcium, and Beta-sitosterol.
Carrots have a long history of human use. For example, lavender carrots were part of the diet of the ancient Greeks and Romans. They were also used for marmalade and carrot wine.
These vegetables are a good source of beta-carotene. They also contain potassium, vitamin A, iron, and manganese. They are good for the immune system and help control blood pressure. Carrots can be eaten raw or cooked. They can be added to soups, salads, and desserts.
The best quality carrots should be brightly colored and smooth. They should also be firm. Good carrots have a slightly sweet taste.
Carrots can be harvested at around four months of growth. If they are harvested too early, they may have a soapy taste.
Carrots are an inexpensive vegetable. They are also low in calories, making them a good choice for those who want to eat healthy without spending a lot of money. They are a good addition to a diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables.
How To Choose Good Carrots?
Choosing good carrots isn’t just about looks. It’s also about the taste. A good carrot should have a crisp texture, as well as a good color.
The best carrots are orange to orange-red, and should be firm and smooth. They should not have cracks or blemishes. Besides their orange color, carrots also contain beta-carotene, potassium, vitamin C, fiber, and anthocyanins.
Carrots are considered a biennial plant, and go through various stages of growth. They first grow leaves in spring. These leaves help the plant obtain energy from the sun. These leaves also help the plant absorb water.
Carrots can be eaten raw or cooked. A good way to preserve carrots is by blanching them in boiling water for two minutes. After cooling, they should be placed in a freezer bag. Then, they’re ready to be stored for up to a year.
To store carrots, make sure you’re getting the best quality. If you’re buying carrots with green tops attached, remove them before freezing. This will prevent premature wilting of the carrot’s roots.
Carrots are a good source of vitamin A, vitamin B1, and beta-carotene. They contain a variety of phytonutrients, including pantothenic acid, hydroxycinnamic acid, and polyacetylenes. Carrots also contain potassium, magnesium, and biotin.
Carrots Are A Vegetable?
Despite their sweet taste, carrots are not really fruits. They are a vegetable, but many people mistake them for fruits. They are also a popular ingredient in recipes. They are delicious and nutritious.
Carrots are a nutritious vegetable that have a variety of health benefits. They are high in fiber, low in calories, and contain several vitamins and minerals. They are also a good source of beta carotene, which helps improve vision and boosts your immune system.
Carrots can be eaten raw or cooked. You can also use carrots as a base for cakes and soups. They keep well in a cold storage environment and will last a long time. They also help promote digestion and protect your skin.
They can also be added to salads for extra nutrients. They also contain carotenoids, which are powerful antioxidants. These compounds have been linked to reducing the risk of many illnesses, including cancer. They also have an anti-inflammatory effect. They are also known to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Carrots have a high water content, which helps maintain a healthy body. They also contain fiber, which can help reduce blood sugar levels.
How To Prepare Carrots
Whether you are looking for a fresh fruit or vegetable to add to your meals, carrots can be a tasty choice. They are delicious when roasted, sauteed or grilled. They are versatile, nutritious and add a burst of color to any dish. They can also be frozen for later use in smoothies and soups.
Whenever you are ready to use fresh carrots, it is important to rinse them well. This will help prevent the carrots from browning. You can also use a vegetable peeler to remove any dirt.
Carrots should be cut into quarters, or a small section, depending on the thickness. They should be sliced thinly to prevent burning. They should be seasoned with salt and pepper to taste.
Carrots should be cooked in boiling water to bring out their natural sweetness. You can also add vegetable stock or chicken stock to the water. This method of cooking breaks down the beta-carotene fiber and makes the carrots more palatable.
Cooking carrots is easy. You can also use frozen carrots for cooking and baking.
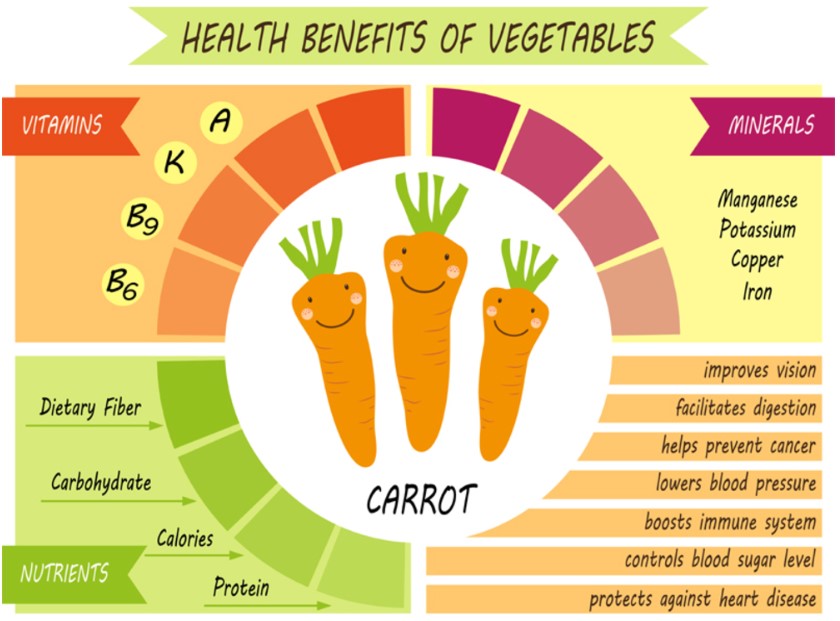
Colored Carrots and Their Health Benefits
Adding colorful carrots to your diet is a great way to get an assortment of vitamins and minerals. They also offer a different flavor to your meals.
These fruits are rich in fiber, vitamin C, and potassium. These nutrients can help protect against heart disease and certain types of cancer. They may also reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Carrots are an easy vegetable to eat and can be cooked or eaten raw. They can be eaten as part of a main dish or added to a salad. They are also popular as a lunchbox treat.
Carrots are an excellent source of fiber, vitamin A, and vitamin C. These nutrients help protect your body from diseases and improve your skin. They also support the growth of tissues and help your immune system. The high amounts of potassium in carrots help to regulate the heartbeat and blood pressure.
These fruits are also rich in vitamin K, which helps blood to clot properly. They are also rich in protein, dietary fiber, and carbohydrates.
Orange Carrots Health Benefits
Whether you choose orange carrots or white carrots, these vegetables are a great source of beta carotene and other antioxidants. These vitamins are important for your skin and eyesight. Carrots can also help fight heart disease and cancer. You can enjoy them cooked or raw. The most common color is orange, but you can also get carrots in a variety of other colors.
Carrots have antioxidant properties that can help you fight the effects of oxidative stress. Too much oxidative stress in your body can cause cancer and heart disease. Carrots contain beta carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin. These antioxidants work together to fight off free radicals. Carrots also contain potassium, which can help lower your blood pressure.
Carrots contain high amounts of fiber, which is beneficial for digestive and weight control. Fiber helps keep your body’s cholesterol levels in the normal range. They can also help regulate your blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Carrots are a good source of vitamins A and B. These vitamins are important for your immune system, which can protect you against cancer. Vitamin A is also important for your skin. Carrots contain beta-carotene, which helps your body make vitamin A. Carrots are also rich in lutein, which can help protect your eyes from cataracts. Carrots also contain calcium and a mineral called magnesium. These minerals are easily absorbed by your body.
- Carrots and Eye Health
During World War II, the British Royal Air Force (RAF) pilots claimed to have improved their night vision by eating carrots. This carrots and eye health claim was part of a propaganda campaign from the Ministry of Food. It resonated with blackout-weary civilians.
Carrots contain lutein, an important antioxidant that helps protect the retina from damage caused by oxidative stress. Lutein helps increase the density of the pigment found in the macula, a yellow oval area in the center of the retina.
Lutein is also important because it helps protect the chromophores in the eye from oxidative stress. In turn, this helps protect the retina from age-related macular degeneration.
Moreover, beta-carotene is a carotenoid that gives many plants their bright colors. It is converted into vitamin A in the body. However, the conversion process is inefficient.
Although carrots are not the best source of vitamin A, they do contain a variety of other eye-friendly nutrients. They also contain antioxidants that may help prevent eye damage caused by free radicals.
Carrots and eye health have been linked for centuries. They may also help with digestion and skin health. But the best way to protect your eyes is to make healthy lifestyle choices. These include eating a balanced diet, avoiding smoking, limiting screen time, and exercising.
- Carrots and Skin Health
Having carrots on a daily basis helps maintain the health of your skin. They are full of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. They prevent free radical damage, reduce dark spots, and enhance skin tone. They also help maintain a clear complexion.
Beta-carotene is one of the most important compounds found in carrots. It acts as an antioxidant, and can protect against the effects of UV radiation. It also promotes the immune system.
Carrots contain vitamin A, which works to maintain healthy skin. Vitamin A promotes collagen synthesis and cell turnover. Vitamin A also helps prevent uneven skin tone and pigmentation.
Carrots contain lutein and zeaxanthin, which help protect the skin from UV damage. Zeaxanthin also reduces inflammation and minimizes damage caused by free radicals.
Carrots also contain vitamin C, which acts as an antioxidant. Vitamin C prevents hyperpigmentation and protects the skin from UV rays. Vitamin C also helps the body produce collagen.
Carrots are also an excellent source of potassium and magnesium, which are important for skin health. These nutrients help the body maintain a healthy digestive system and provide energy to the body.
- Carrots and Lung Health
Various studies have shown that a diet rich in carrots can reduce the risk of lung cancer. Carrots are high in carotenoids and antioxidants. These compounds are known to help with lung health, and may also aid in memory and cognitive function.
The lutein in carrots can also reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration. The antioxidant beta-carotene helps with eye health, and protects against cataracts. Carrots are also an excellent source of vitamin C. Vitamin C helps the body produce collagen, which is essential for keeping the body healthy.
Researchers have also found that carrots can help protect the lung from damage from cigarette smoke. In fact, a recent study conducted by Harvard researchers found that those who ate foods rich in tomatoes and carrots had a lower lung cancer risk.
Carrots are an excellent source of vitamin C and potassium. They can also improve digestion and blood sugar regulation. They also contain various B vitamins and traces of iron.
Carrots are a good source of fiber, and have been shown to help support digestive health. A high-fiber diet may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. They also contain a substance called indole-3-carbinol, which can help repair damaged cells.
- Carrots and Mental Health
Several studies have shown that carrots have positive effects on mental health. They are high in nutrients and antioxidants, and have been shown to help with a variety of illnesses.
Carrots are one of the highest vitamin A providers in the world. They are also high in fiber, which helps the body eliminate excess cholesterol.
Studies have shown that carrots contain antioxidants that prevent oxidation-related illnesses, such as heart disease. Carrots also fight bacteria in the mouth, removing plaque and improving the appearance of teeth.
Carrots are also rich in beta-carotene, which has been shown to be a powerful cancer fighter. Boosting beta-carotene consumption can cut the risk of lung cancer by almost 50%. Beta-carotene is also thought to help the body fight free radical damage. It also has antioxidant properties that help with memory and cognitive function.
In addition to the antioxidant benefits, carrots also contain several nutrients that support the immune system. They contain vitamin A, which supports the normal development of the cornea and epithelial cells. Vitamin A also helps with maintaining normal cellular communication. Deficiency of vitamin A can lead to progressive eye disease.
Red Carrots Health Benefits
Whether you’re eating carrots raw or cooked, you can benefit from the health benefits of carrots. The nutrients in carrots can help you maintain a healthy weight, lower your blood sugar and protect you from chronic diseases. The nutrient-rich carrots also support your immune system.
Carrots are rich in a variety of antioxidants, including beta carotene, lutein and lycopene. These nutrients protect your eyes, skin and heart from free radical damage. They also lower the risk of developing certain cancers, such as breast and colon cancer. They also help keep blood pressure in check and decrease your risk of heart disease.
Beta carotene, also known as vitamin A, is an important antioxidant that helps protect your eyes from light damage. In addition, it helps protect your immune system from infections and maintains the health of your cornea. Vitamin A is also important for maintaining healthy mucous membranes. The cells in these membranes are important entry points for pathogens and contribute to your body’s immune system response.
Besides its antioxidant effects, beta carotene can also affect your metabolism. It can lower your risk of developing diabetes and may affect the way your immune system fights infection. It can also improve cognitive function.

Yellow Carrots Health Benefits
Adding carrots to your diet can help you boost your vision, boost your brain health, and improve your heart health. Carrots are full of vitamins and antioxidants, and are low in calories.
Carrots are also high in fiber, which may help lower blood pressure. They also contain a good amount of vitamin A, which helps the body build and protect its immune system. In addition, carrots contain vitamin K, which helps blood clot correctly and keep your blood calcium levels in check.
Carrots also contain anthocyanins, a powerful antioxidant. These antioxidants may help protect your eyes from age-related macular degeneration. They also protect your eyes from cataracts.
Carrots also contain lutein, a type of Vitamin A. Lutein protects your eyes, and helps to keep them young. It also protects your retina and lens. A deficiency in lutein can lead to age-related macular degeneration. Carrots are also high in beta-carotene, an antioxidant pigment. This pigment helps protect your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays.
Beta-carotene may also help prevent prostate cancer. It is also associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer. Carrots also contain lycopene, a powerful antioxidant. Lycopene may also help prevent heart disease.

Purple Carrots Health Benefits
Adding purple carrots to your diet is an easy way to get some important nutrients, antioxidants and medicinal benefits. Purple carrots are rich in minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber. They are also low in calories, which makes them a great choice for a healthy diet. Besides, they are a great addition to many different meals.
Purple carrots contain a large amount of antioxidants called anthocyanins. These pigments give the carrot its distinctive color. The anthocyanins are also thought to give carrots their anti-inflammatory properties. These properties can help improve cognitive function, improve memory, and protect against eye diseases.
In addition to these benefits, purple carrots have also been found to lower cholesterol levels. This makes them a great choice for people looking to improve their heart health. Purple carrots are also good for preventing metabolic syndrome, a condition that increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Besides, purple carrots are rich in antioxidants, vitamin E and group B vitamins. These antioxidants are thought to counteract enzymes that damage blood vessels. Also, they increase the immune system.

White Carrots Health Benefits
Those looking for nutritional benefits of white carrots can be pleased to learn that these vegetable varieties are packed with antioxidants and fiber. They are also high in vitamin A and several minerals. These nutrients can have a positive impact on the immune system and the digestive system. Adding them to your diet can also protect your eyes.
Carrots also contain potassium. This mineral helps relax blood vessels and reduce the risk of high blood pressure and cardiovascular problems. Also, the fiber in carrots can help improve digestive health. In addition, the fiber can help prevent type 2 diabetes.
Eating carrots regularly may also protect your eyes. Carrots contain lutein and zeaxanthin, which help protect your retina and lens. These nutrients also help prevent age-related macular degeneration.
Beta-carotene, a compound found in carrots, is a potent antioxidant. Beta-carotene is converted by the body into vitamin A, which plays an important role in the eyes, immune system, and metabolism. In addition, it can help the eyes fend off UV light from the sun.

Conclusion
Among the carrot family, the carrot storage root is a good source of vitamins, antioxidants, and minerals. Hence, its merits merit a study in their own right.
As you may have guessed, the carrot is a member of the genus apium. Carrots belong to the flowering plant family Apiaceae, and are one of the few genuses to boast both a leaf and a stem. The carrot genus is the second largest in the family, and the third most diverse. Its popularity stems from the carrot’s taste and health benefits.
Carrots are one of the few plants in the Apiaceae family to be native to North America. The “Western” carrot arose in the Netherlands during the seventeenth century. Its popularity has only grown in the past two centuries, and now ranks as one of the largest vegetable producers in the world. Its reputation as a good source of nutrition is bolstered by the recent discovery that it has the highest antioxidant activity of any known vegetable.
Molecular techniques have revealed a rich storehouse of information about vegetable crops, including the carrot. In particular, the carrot’s ability to produce carotenoid molecules has led to the discovery of many novel and useful compounds, which have been used as additives and preservatives in a wide variety of applications.
